Incremental Loads
Incremental Loads
Handling Incremental Loads in CRESTONE
When working with large datasets in SAP and external systems, it is often inefficient to extract the entire dataset every time. Instead, incremental loads allow you to capture only the records that have changed since the last successful extraction. CRESTONE provides multiple alternatives to implement incremental strategies depending on the business scenario, data source, and technical requirements.
1. Using Date or Timestamp Fields
If the source table or view includes a timestamp or last-change field (for example, ERDAT, AEDAT in SAP), CRESTONE can automatically filter the extraction based on dynamic date variables.
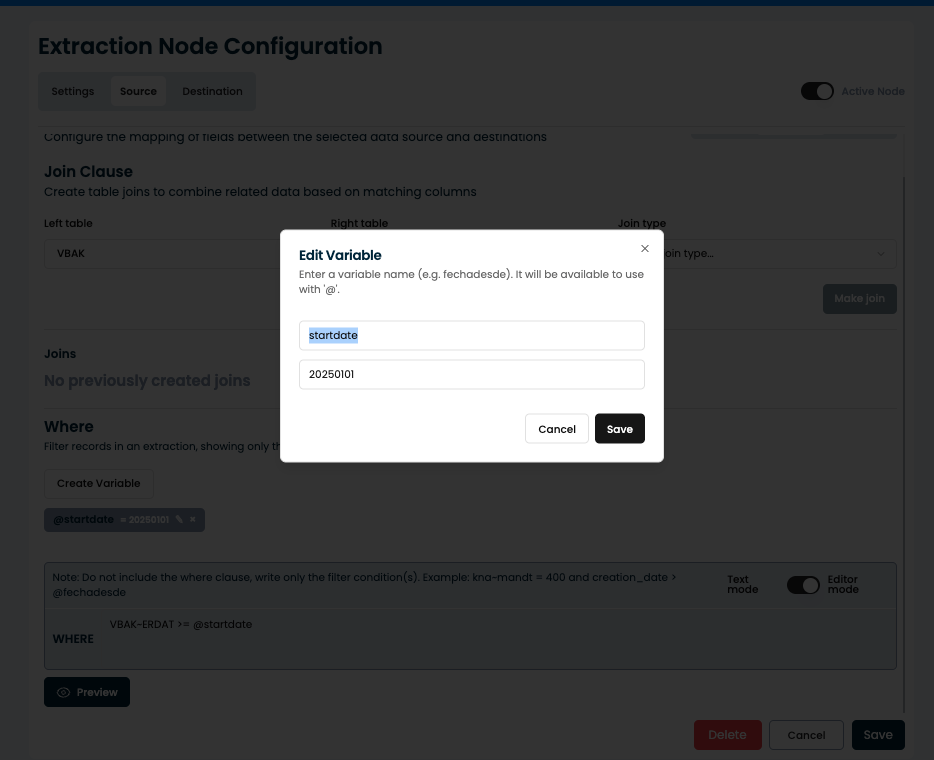
🔧 Configuration in the Extraction Node
In the Source tab of an Extraction Node:
- Create variables to represent your desired date range.
- Assign them dynamic expressions using Python syntax wrapped in
{{ ... }}. - Reference those variables in the WHERE clause to control which records are extracted.
For example:
| Variable | Expression | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
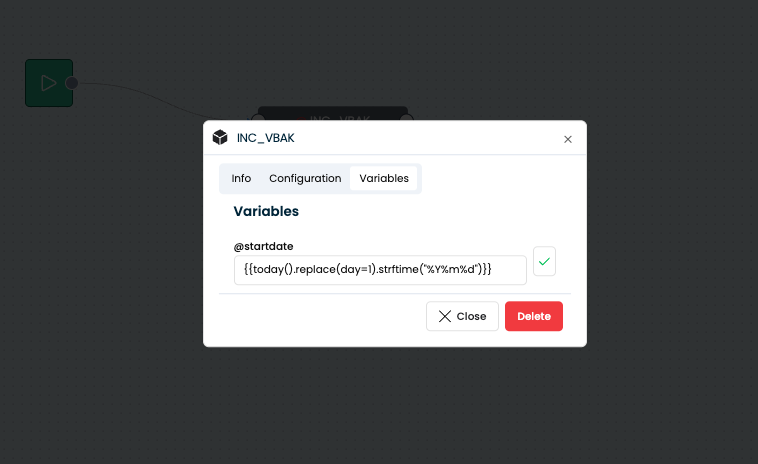
@startdate | {{today().replace(day=1).strftime("%Y%m%d")}} | First day of the current month |
@enddate | {{(today().replace(day=1) - timedelta(days=1)).strftime("%Y%m%d")}} | Last day of the previous month |
WHERE Example:
VBAK-ERDAT >= @startdate
CRESTONE will automatically resolve these variables at runtime during extraction.
✅ Advantages
- Simple and flexible — the logic is embedded directly in the extraction node.
- Allows dynamic filtering without manual date updates.
- Ensures consistency when scheduling incremental or monthly loads.
⚙️ Considerations
- The date expressions must be valid Python syntax (evaluated within CRESTONE’s runtime).
- The timestamp field used in the filter (e.g.,
ERDAT,AEDAT) should be reliably updated and indexed in the source system. - For historical loads, you can define static values (e.g.,
20250101) before switching to dynamic expressions. - To avoid potential duplicates, ensure that the destination table is refreshed or truncated appropriately before each incremental load, especially when overlapping date ranges are used.
2. Delta Extraction with SAP Standard Extractors
For certain SAP modules (FI, CO, MM, SD, etc.), SAP provides standard delta-enabled extractors (e.g., 2LIS_11_VAHDR, 2LIS_02_HDR, 0FI_AR_4).
These extractors implement native SAP delta logic using delta queues and change pointers.
CRESTONE integrates directly with these extractors through an RFC connection, allowing automatic retrieval of only new or changed records.
🔧 Configuration in CRESTONE
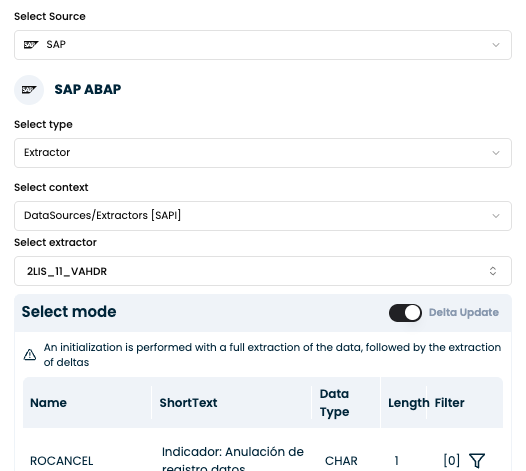
In the Extraction Node Configuration, select:
- Source:
SAP ABAP - Type:
Extractor - Context:
DataSources/Extractors [SAP] - Extractor: e.g.,
2LIS_11_VAHDR(Sales Document Header)
Once selected, the node automatically detects whether the extractor supports delta mode.
When Delta Update is enabled, CRESTONE performs:
- Initialization — a full extraction of existing data.
- Delta Loads — subsequent extractions only for new or changed records.
During initialization, CRESTONE registers a subscription in SAP’s delta mechanism.
You can monitor its status in the node’s Delta Config tab:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Subscription ID | Unique identifier for the delta subscription in CRESTONE |
| Subscription name | Logical name used to identify the delta process |
| Pointer | Stores the last extraction checkpoint (SAP delta pointer) |
| Last execution | Timestamp of the last successful extraction |
Example (from CRESTONE UI):
Subscription ID: CRb058ffd2-abc6-4ebe-9f2b-fac7fe048591
Pointer: 20251012003005.000000000
Last execution: 12/10/2025 00:30:05 UTC
This ensures each extraction continues from the last processed delta, maintaining data consistency across runs.
✅ Advantages
- SAP-native approach with built-in delta logic.
- Automatically tracks new and changed records using SAP delta queues.
- Reduces development and maintenance effort.
- Integrates seamlessly with CRESTONE’s control tables for pointer management.
⚙️ Considerations
- Not all extractors support delta updates.
- The delta queue (
RSA7) must be properly initialized and monitored in SAP. - A reinitialization may be required if the pointer is deleted or if data inconsistencies occur.
🧩 Common Examples of Delta-Enabled Extractors
| Module | Extractor | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SD | 2LIS_11_VAHDR | Sales Document Header |
| SD | 2LIS_11_VAITM | Sales Document Item |
| MM | 2LIS_02_HDR | Purchase Order Header |
| MM | 2LIS_02_ITM | Purchase Order Item |
| FI | 0FI_GL_4 | General Ledger Line Items |
| FI | 0FI_AR_4 / 0FI_AP_4 | Accounts Receivable / Payable Line Items |
| CO | 0CO_OM_CCA_1 | Cost Centers – Actual Costs |
🧭 Delta Pointer Management
CRESTONE provides a built-in interface to control and monitor the delta pointer directly from the Delta Config tab:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Delete subscription | Resets the delta initialization. The pointer is set to zero and removed from the control table. Used when you need to reinitialize the extractor. |
| Update delta without extraction data | Updates the delta pointer in CRESTONE to match the current SAP delta position without extracting new records. Useful for synchronization or skipping erroneous deltas. |
| Preview | Displays a simulation of the next delta load, showing which records would be included before execution. |
This management layer provides transparency and control over the delta lifecycle, without requiring access to transaction RSA7 or RSA3 in SAP.
🧩 Typical Flow in CRESTONE
- Initialization: full data extraction → subscription and pointer created.
- Delta load: fetches only new/changed records since last pointer.
- Monitoring: pointer automatically updated after each successful run.
- Reinitialization: manual pointer reset if needed.
With this setup, CRESTONE ensures robust, auditable, and fully automated delta extraction for SAP standard extractors.

3. Table Change Data Capture (CDC) with SAP Change Documents
CRESTONE supports Change Data Capture (CDC) using SAP’s change-document framework and control tables (CDHDR, CDPOS) or via direct table-level pointers for standard master and transactional data.
This approach tracks inserts, updates, and deletes performed on business objects or tables for which change tracking is active in SAP.
🔧 Configuration in CRESTONE
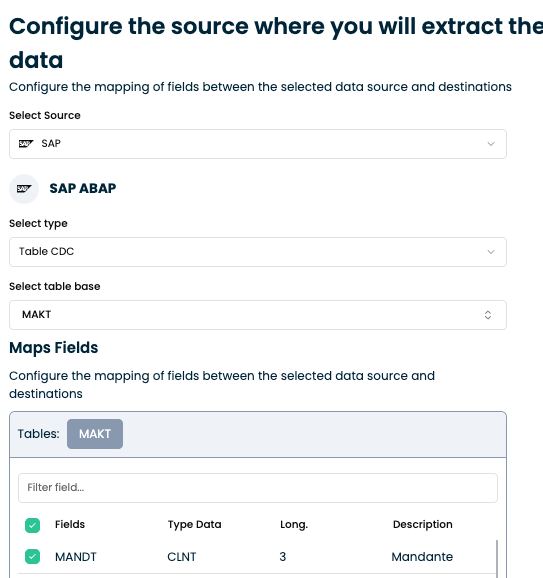
In the Extraction Node Configuration, select:
- Source:
SAP ABAP - Type:
Table CDC - Base Table: e.g.,
MAKT(Material Descriptions)
CRESTONE will automatically map the table fields and enable CDC Config mode, where a pointer is maintained for incremental extraction.
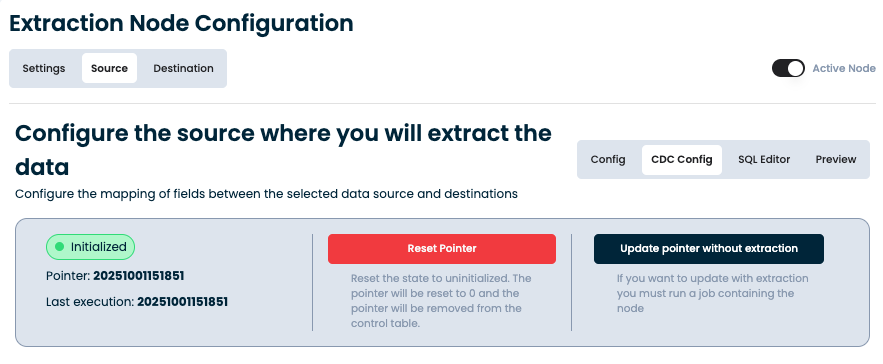
Once the initial load (initialization) is executed, CRESTONE stores a pointer that represents the last successful extraction timestamp:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Pointer | Indicates the last record processed or timestamp used for CDC continuation. |
| Last execution | Timestamp of the last successful CDC run. |
| Status | Shows whether the CDC process is Initialized or pending. |
Example (from CRESTONE UI):
Pointer: 20251001151851
Last execution: 20251001151851
Status: Initialized
This ensures that only new or modified records since the last pointer are captured in subsequent extractions.
🧭 CDC Pointer Management
CRESTONE provides a control interface similar to delta extractors to manage the CDC pointer lifecycle:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Reset Pointer | Reinitializes the CDC process by resetting the pointer to zero and clearing its record from the control table. Use this when a full reload is required. |
| Update Pointer without Extraction | Updates the pointer position without performing a data extraction. Useful for synchronization or skipping a known data window. |
This allows users to manually control or realign the CDC process without SAP GUI access.
✅ Advantages
- Captures both new and modified records with high accuracy.
- Fully aligned with SAP change-document logic, ensuring consistency with business transactions.
- Maintains an internal pointer for efficient incremental loads.
- Can be applied to master data (e.g.,
MARA,MAKT,KNA1) or transactional data (e.g.,VBAK,VBRK) where CDC logic is available.
⚙️ Considerations
- Requires that change-document tracking is enabled for the corresponding SAP object.
- Not available for all tables — only those registered in SAP’s change-document framework or those compatible with table-based CDC logic.
- May introduce additional system load on very active change tables.
- Proper pointer management is essential to prevent duplication or data gaps.
By leveraging Table CDC, CRESTONE provides a granular, low-latency mechanism to detect and replicate data changes from SAP tables, ensuring near real-time synchronization without requiring a full data reload.
4. Hybrid Approaches
In complex environments, a combination of strategies may be applied. For example:
- Use timestamps for master data tables.
- Use SAP Standard Extractors for transactional data.
- Use CDC with change documents for objects requiring full history of changes.
✅ CRESTONE’s incremental load framework adapts to any SAP module — from simple master data updates to complex transactional histories — while minimizing data transfer and ensuring consistency across loads.