Extractors
Extractors
Configuring a Node for SAP ABAP Extractors
When setting up a node to extract data from SAP using an ABAP extractor, you’ll follow a series of steps to define the source, context, and extraction parameters. This setup is essential to ensure that data is retrieved correctly and efficiently from the SAP environment.
1. Select Extractor Type
Start by indicating that the type of extraction is an “Extractor.” This sets the node to expect SAP-compatible structures and logic, such as delta-enabled extractions.
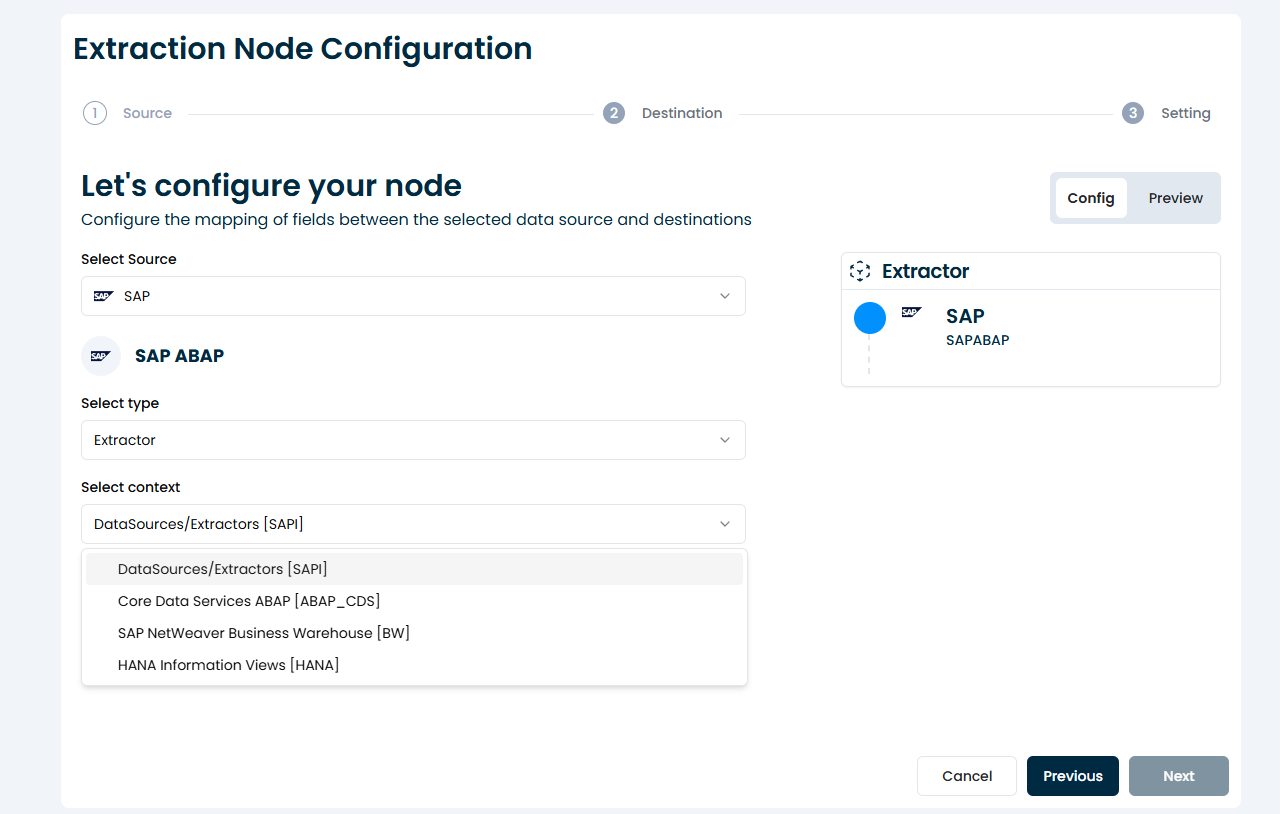
2. Choose the Context
Select the context in which your extractor operates. Available options include:
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Datasource / Extractor (SAPI): | Traditional SAP extractors from the SAPI framework. |
| Core Data Service ABAP (ABAP_CDS): | CDS views that offer modern modeling features. |
| SAP Change Data Capture (ABAP_CDC): | For real-time or near-real-time change tracking. |
| NetWeaver Business Warehouse (BW): | Extractors from SAP BW systems. |
| HANA Information Views (HANA): | Views from HANA native environments. |
The selected context determines the available extractors and supported configuration features.
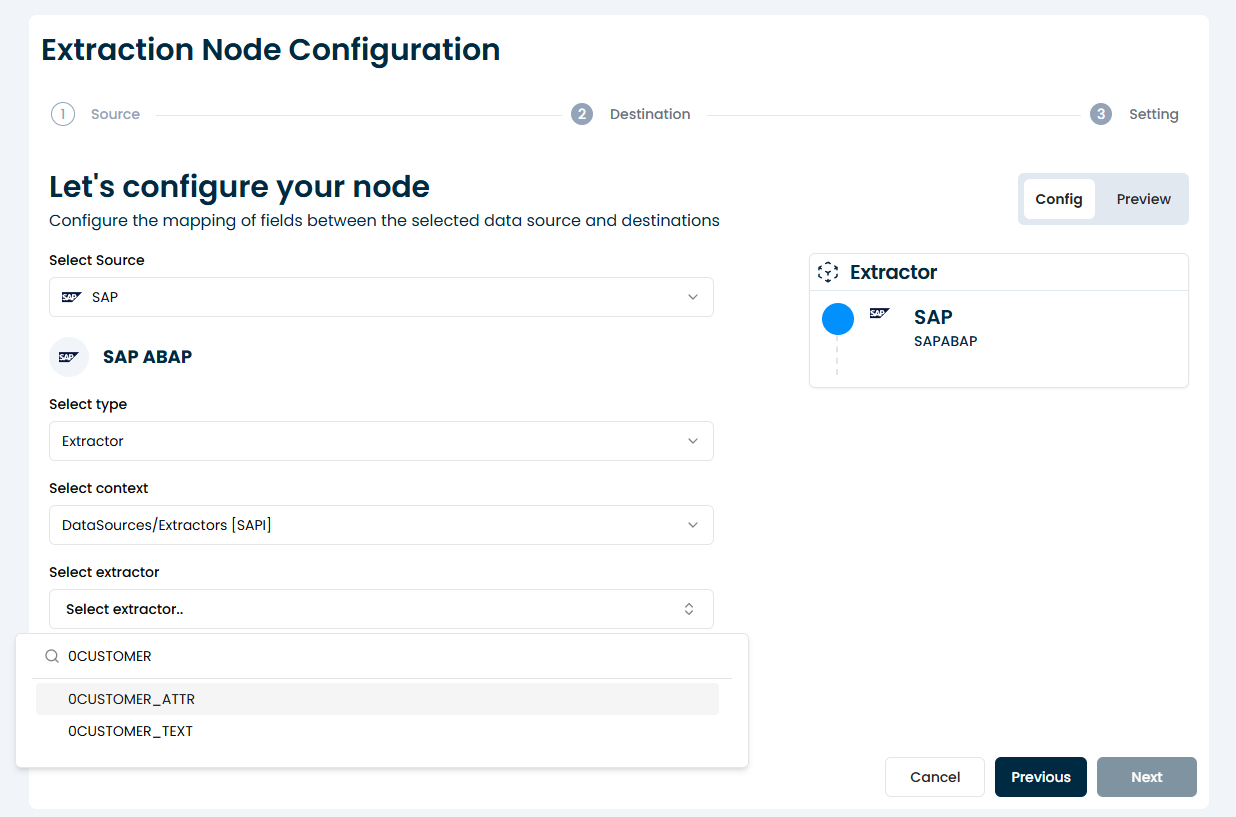
3. Select an Extractor
Once the context is chosen, you’ll be prompted to choose the specific extractor from a list provided by the system. This is typically a list of extractors available based on your SAP connection and credentials.
4. Add Variables
You can now add variables to parameterize the extractor.
🛈 Reminder: Use variables to filter or scope the data extraction — for example, by date, company code, or region. These variables are passed as input parameters to the extractor.
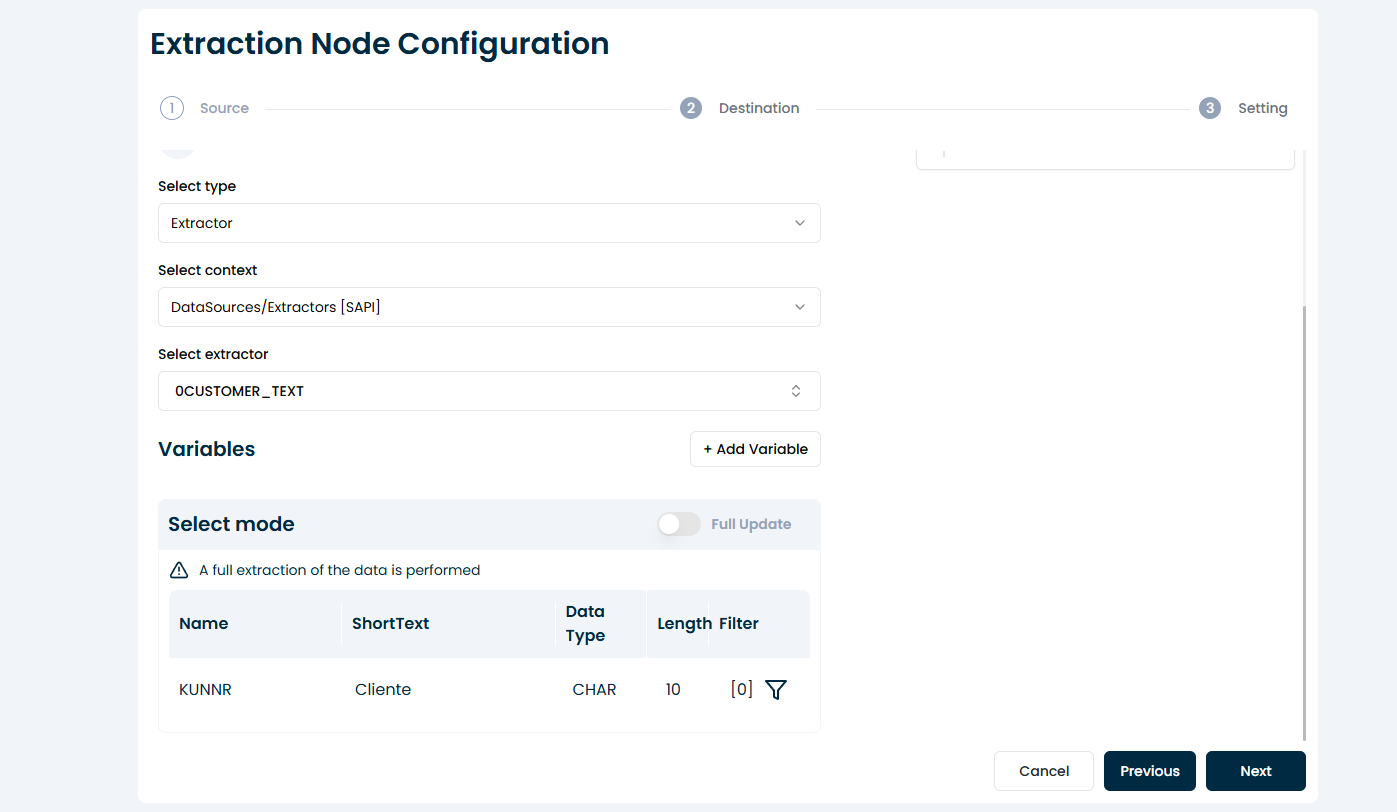
5. Select Load Mode
Choose how the data will be extracted:
-
Full Load: Extracts the entire dataset each time.
-
Delta Load: Extracts only new or changed records since the last execution (only available for delta-enabled extractors).
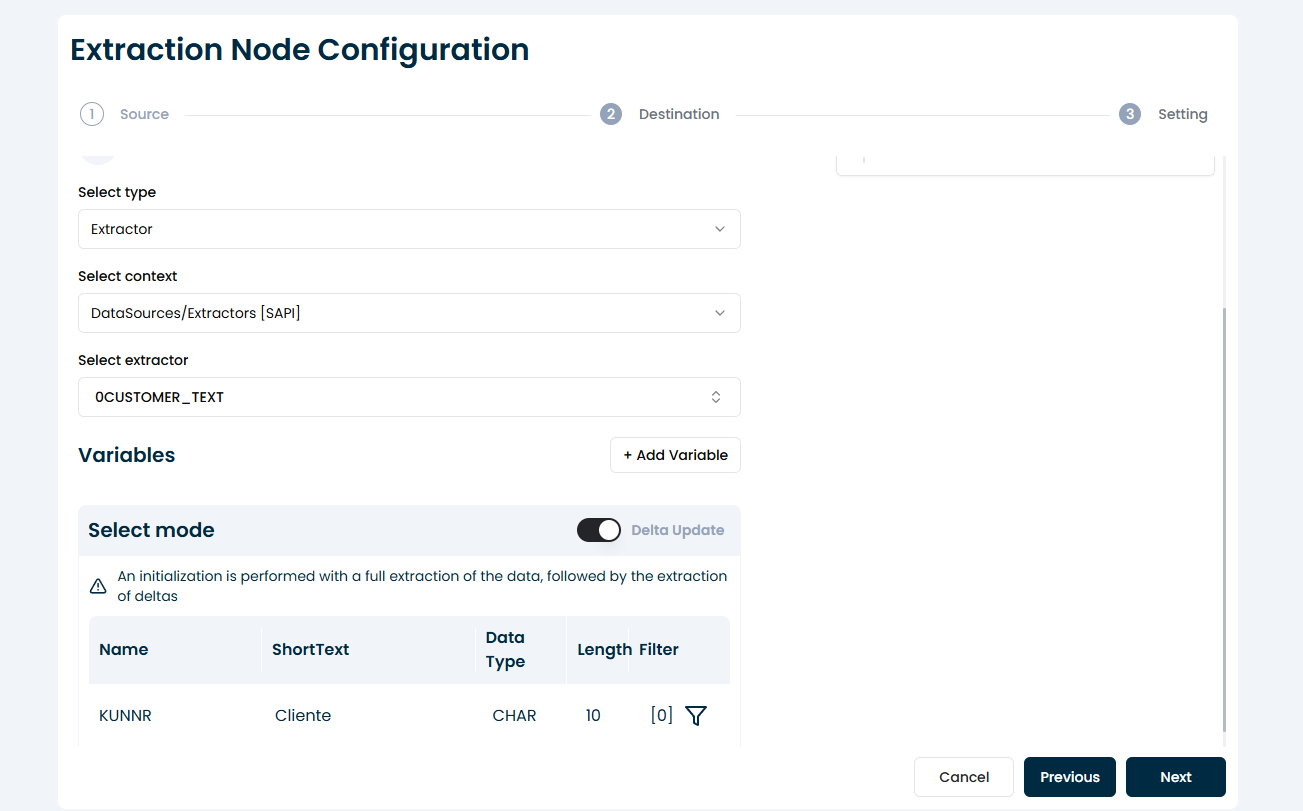
Delta mode is ideal for performance and incremental updates in recurring extractions.
6. Edit Filters (Optional)
You may configure filters to restrict the dataset returned by the extractor.
🛈 Reminder: Filters allow you to narrow down the result set directly within the extraction logic — this is useful for optimizing performance or testing smaller data slices.